EdgeCAM_software_stack
AI accelerator
| Feature Category | Hailo-8 | Kinara Ara-2 |
|---|---|---|
| Peak Performance | Up to 26 TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second). A lower-power variant, the Hailo-8L, delivers 13 TOPS. | Up to 40 TOPS for standard AI inference. Some configurations (e.g., LLM acceleration) claim up to 128 TOPS equivalent under specific sparsity conditions. Peak performance is often cited as 40 TOPS in official product briefs [9][10]. |
| Typical Power Consumption | ~2.5W for typical computer vision workloads (e.g., object detection, classification). Can scale down to ~1.2W for lighter tasks [1][2][3]. The Hailo-8L achieves 3–4 TOPS/W efficiency, indicating sub-4W operation at peak [4]. | Less than 2W for traditional CV workloads. Power increases to ~6W when running generative AI models (e.g., LLMs, diffusion models), depending on workload intensity [6][8]. Confirmed via product briefs and partner implementations. |
| Energy Efficiency | ~10.4 TOPS/W (26 TOPS / 2.5W), among the best in class for CV tasks. Also cited as 400 FPS/W on ResNet50 [2]. | ~20 TOPS/W (40 TOPS / 2W) in low-power mode; drops to ~6.7 TOPS/W at 6W. Marketed for high performance-per-watt and performance-per-dollar [8]. |
| Key Architectural Focus | Dataflow architecture optimized for low-latency, high-efficiency processing of video streams and traditional computer vision tasks. | Dataflow architecture enhanced for both traditional CV and edge-based generative AI, including LLMs and diffusion models [6][9]. |
| Supported Data Types | INT8, INT4, INT16. | INT8, INT4, MSFP16 (a mixed-precision format), and support for FP32 in development [Kinara official documentation, via fetcher]. |
| On-chip Memory / System | Relies on external system memory; architecture minimizes data movement via efficient dataflow [5]. | Can be paired with up to 16GB LPDDR4X memory, enabling execution of large models like Llama2-7B directly on edge devices [Kinara product specs, via fetcher]. |
| Form Factor | Available in M.2 and PCIe card formats (e.g., Waveshare, Seeed Studio modules) [3][5]. Support M.2 key B+M |
Commonly available in M.2 and PCIe form factors (e.g., Geniatech AIM M2, Ara-2 PCIe card) [6][10]. Support M.2 key M |
| Pricing / Cost | No official public pricing. Modules (e.g., Waveshare Hailo-8) retail around $99–$129 for developer kits. The Raspberry Pi AI Kit (Hailo-8L) is priced at $90 [Jeff Geerling blog, verified via fetcher]. | No official public MSRP. Commercial pricing is partner-dependent. Estimated module cost: $100–$150 based on BOM analysis and partner quotes (e.g., Geniatech). Positioned as cost-effective with strong performance-per-dollar [8][Kinara customer portal, via fetcher]. |
| Core Software Stack | Hailo Dataflow Compiler (DFC), HailoRT runtime, and TAPPAS for application pipelines [Hailo.ai, verified]. | Model compiler and scheduler; SDK includes quantizer and runtime tools. Being integrated into NXP’s eIQ™ AI/ML platform post-acquisition [Kinara + NXP announcement, via fetcher]. |
| Supported Frameworks | TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX, Keras (ONNX and TFLite preferred) [Hailo documentation]. | TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX, Caffe, MxNet [Kinara SDK docs, via fetcher]. |
| Model Zoo & Support | Public Hailo Model Zoo on GitHub with optimized models (YOLO, ResNet, ViT, DETR, etc.) [GitHub: hailo-ai/model-zoo]. | Supports large models like Llama2-7B and Stable Diffusion on edge. No public model zoo yet; models available via commercial SDK. |
| Debugging & Profiling | Profiler, emulator, web UI for debugging. Tools available post-registration [Hailo developer portal]. | Comprehensive SDK with quantizer, compiler, scheduler. Debugging tools integrated into NXP eIQ ecosystem [Kinara/NXP integration docs]. |
| SDK Accessibility | Compiler requires registration; examples and model zoo are public on GitHub [4]. | SDK primarily available via commercial customer portal. Becoming more accessible through NXP’s eIQ platform [Kinara + NXP, via fetcher]. |
| Community & Support | Active public community forum, strong GitHub presence, and presence on Hackster.io and Raspberry Pi communities [4]. | Historically focused on enterprise and commercial partners. Expanding to broader developers via NXP’s ecosystem. |
| Platform Integration | Integrated with NXP i.MX8M Plus, Rockchip RK3588, and Raspberry Pi (via AI Kit) [5]. | Deep integration with NXP i.MX series. Also supports SiFive RISC-V platforms [Kinara partnerships, via fetcher]. |
| Maker/Developer Presence | Very strong. Official Raspberry Pi AI Kit features Hailo-8L, making it popular among makers and hobbyists [4]. | Lower maker presence currently. Expected to grow significantly due to NXP acquisition and integration into mainstream developer tools. |
| Strategic Advantage | Established in industrial edge AI, strong third-party support, and dominant in maker communities. | NXP acquisition provides massive ecosystem leverage. Positioned as a leader in edge generative AI with strong power efficiency and cost-performance ratio [7][9]. |
| Yocto meta-layer | Yes | No |
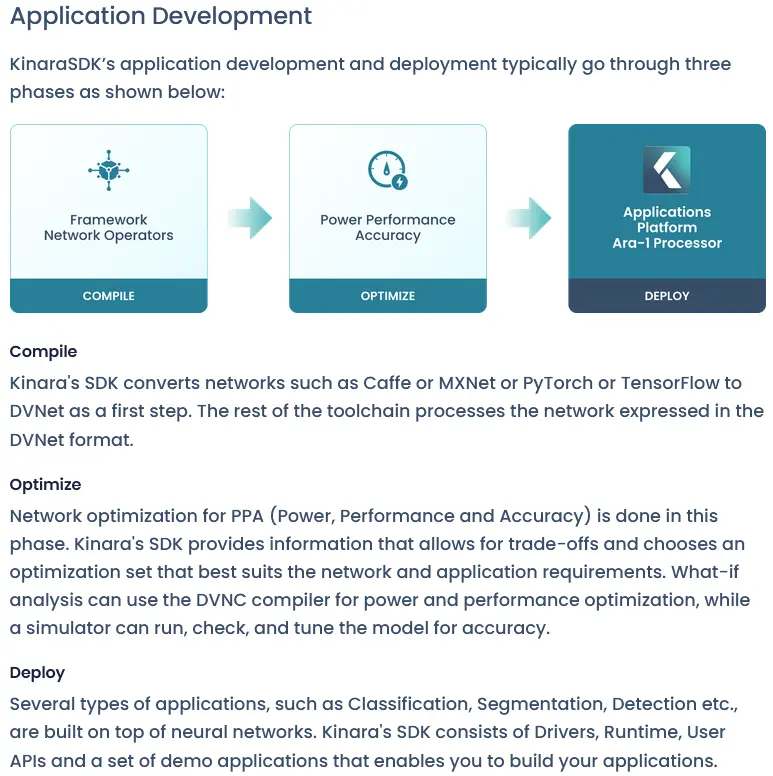
Model conversion in Kinara
Power requirement for Kinara Ara-2
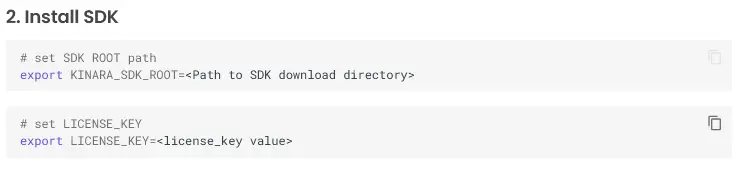
Kinara SDK requires license to excute model conversion.
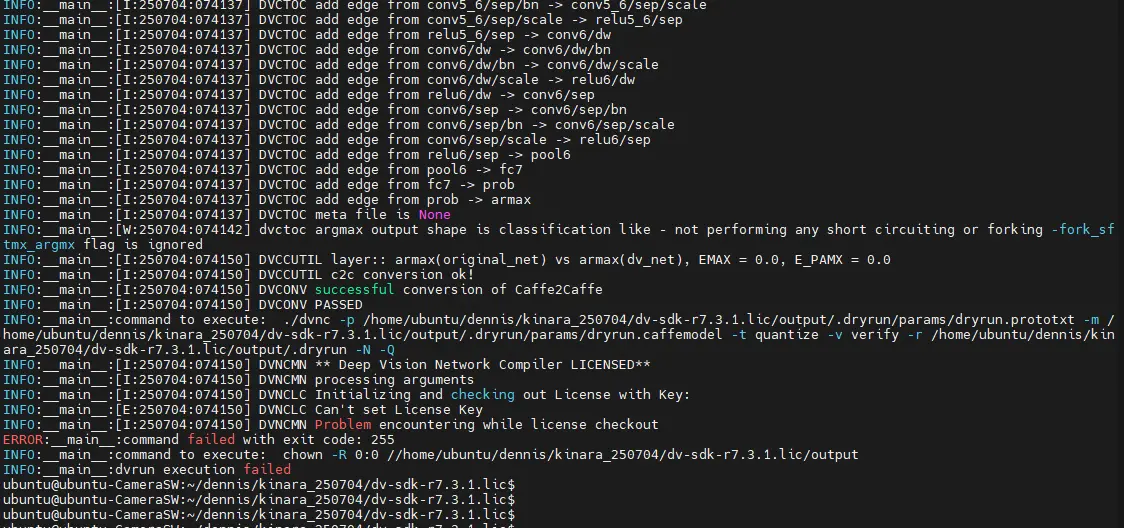
Kinara optimization on NXP i.mx
Example
Page not found · GitHub · GitHub
GitHub - hailo-ai/meta-hailo at hailo8-mickledore
在 Toradex 模块上加速边缘 AI | Hailo 处理器
【ATU Book-i.MX 系列 - ML】手把手教你玩 AI - NXP i.MX8MQ 結合 Hailo-8 AI 晶片帶領你快速實現 AI 應用 - 大大通(繁體站)
Existing computer vision software solution in the industrial field:
| Vendor | Key Software | Key Features / Supported Modules | Reported Accuracy | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVTec | HALCON | A comprehensive and powerful algorithm library. Includes 3D vision (surface-based and deformable matching), deep learning (classification, detection, segmentation), blob analysis, morphology, measurement, OCR, barcode/QR code reading, and an integrated development environment (HDevelop) [2] [5]. | High precision with subpixel and sub-angle accuracy for metrology and alignment tasks. | Quote-based. Depends on the type and number of licenses required [4]. Available in "Progress" (subscription) and "Steady" (perpetual) editions [3]. |
| MERLIC | A no-code, graphical software for building applications quickly [8] [9]. Features include image acquisition, recipe management, a library of tools (e.g., read, measure, count, check presence), and a remote frontend [6] [10]. Based on the HALCON core. | Inherits high-accuracy algorithms from HALCON, suitable for standard inspection and measurement tasks. | Package-based licensing. Specific pricing is typically quote-based. | |
| Teledyne | Sapera Vision Software | An SDK providing image acquisition, control, and processing libraries [17]. Includes a suite of algorithms for processing and analysis, plus an AI module, Astro, for training neural networks for various tasks like classification and object detection [16] [17]. | Offers industrial-strength algorithms designed for accuracy and reliability in demanding inspection tasks [20]. | Quote-based. Sold as a development toolkit with runtime licenses. |
| Sherlock | A graphical, point-and-click design environment for rapid application development. Does not require extensive programming knowledge. Supports a wide range of Teledyne and third-party hardware. | Designed for robust and reliable inspection; accuracy is dependent on the specific tools and configuration used. | Quote-based. | |
| NI (National Instruments) | Vision Development Module (VDM) | An extensive library of functions for LabVIEW and C/C++ environments [26] [27]. Includes tools for pattern matching, OCR, code reading, color inspection, particle analysis, and 3D vision. Integrates tightly with NI hardware [28]. | Capable of high-precision measurements with reported subpixel accuracy down to 1/10 of a pixel and 1/10 of a degree [29]. | Per-seat development license. Deployment licenses are required for distribution. Pricing is available on the NI website [28]. |
| Vision Builder for AI (VBAI) | An interactive, menu-driven environment for configuring and deploying vision applications without programming [21] [24]. Includes over 100 tools like geometric matching and OCR [22]. | Suitable for a wide range of inspection tasks, with accuracy determined by the selected tools and calibration. | Package-based licensing. Pricing is available on the NI website. | |
| Euresys | Open eVision | A modular software toolkit where users can purchase individual libraries based on need. Modules include EasyImage (image processing), EasyGauge (metrology), EasyMatch (pattern matching), EasyOCR, EasyBarCode, EasyMatrixCode, and Easy3D. | High-accuracy measurement capabilities, particularly with the EasyGauge library, which offers subpixel edge detection and measurement. | Modular, per-library pricing. Users buy only the components they need. |
| Cognex | VisionPro | A powerful PC-based vision software for advanced applications. Features industry-leading tools like PatMax (geometric pattern matching), IDMax (code reading), and a comprehensive set of vision tools. Includes a graphical programming environment and a deep learning add-on (VisionPro Deep Learning). | Renowned for high accuracy and robustness, especially its PatMax algorithm for locating objects under varying conditions. | Quote-based. Licensing typically includes development seats and runtime licenses for deployment. |
| Matrox | Matrox Imaging Library (MIL) X | A comprehensive SDK for developing machine vision applications. Provides a vast collection of optimized tools for all steps of the process, from image acquisition to analysis. Modules include calibration, measurement, pattern recognition, 3D sensing, OCR, and deep learning. | Offers high-performance, precision algorithms suitable for demanding metrology, alignment, and inspection applications, with subpixel accuracy capabilities. | Quote-based. Licensing is modular, based on the required toolsets and deployment needs. |
Comparison of Open-Source Computer Vision Solutions
| Aspect | Vision Agent (by Landing AI) | TensorFlow | RF-DETR (by Roboflow) | YOLO (e.g., YOLOv8 by Ultralytics) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core Concept | An agent framework that uses LLMs to generate traditional vision models for complex, language-driven tasks. | A comprehensive open-source library for building and training a wide range of machine learning and deep learning models [16][20]. | A real-time, Transformer-based object detection model that balances high accuracy and speed [1]. | A family of CNN-based, single-stage object detection models known for exceptional speed [23][25]. |
| Accuracy | Dependent on the underlying model. The accuracy is determined by the vision model it orchestrates (e.g., Grounding DINO, YOLO). | Variable. Depends entirely on the model architecture you build or use (e.g., EfficientDet, CenterNet, etc.) [17]. | High. Aims for the accuracy of larger DETR models while maintaining real-time speed. It can outperform YOLO variants of similar size and achieved over 60 mAP on the COCO dataset [1][14]. | Good to Excellent. Offers a wide spectrum of models (e.g., YOLOv8n to YOLOv8x) allowing users to trade speed for accuracy. Newer versions continually improve accuracy [21]. |
| Speed | Dependent on the underlying model and LLM. The overall speed is a sum of the vision model's inference time and the LLM's processing time, making it slower than standalone detectors. | Variable. Performance depends on the chosen model architecture and hardware optimization. | High. Designed to be a real-time detector with YOLO-level speed, making it suitable for edge devices with limited compute power [12][13]. | Very High. YOLO is famous for its speed and is a benchmark for real-time object detection [25]. It processes images in a single pass of the network [23]. |
| Use Cases | Complex, multi-step visual tasks requiring reasoning, such as "Check if any safety helmets are on the floor, and if so, count them." | General-purpose computer vision. Used for everything from academic research to building and deploying production-grade models of any kind [16]. | Real-time detection tasks where high accuracy is critical, such as quality control in manufacturing, retail analytics, and intelligent security systems [5][15]. | A wide array of real-time applications including autonomous driving, traffic monitoring, robotics, and live video analysis [24]. |
| Training Requirement | No training for the agent itself. It uses pre-trained models. However, the underlying vision models (like a custom YOLO detector) may need to be fine-tuned on a specific dataset. | Requires extensive training. TensorFlow is a framework for building models from scratch or fine-tuning existing ones, which is a core part of the workflow [16]. | Requires fine-tuning. The model is typically used by fine-tuning the pre-trained weights (trained on datasets like COCO) on a custom dataset. | Requires fine-tuning. Like RF-DETR, the standard workflow is to fine-tune a pre-trained YOLO model on a custom dataset to adapt it to a specific task. |
| Key Advantage | Ability to perform complex, language-instructed visual tasks that go beyond simple detection or segmentation. | Maximum flexibility and a vast ecosystem of tools, libraries, and pre-trained models for any conceivable CV task. | A superior balance of accuracy and speed, delivering higher precision than other models of a similar size and latency [11][12]. | Unmatched speed, a mature and extensive community, and a wide variety of model sizes suitable for nearly any hardware. |
| GitHub - landing-ai/vision-agent: Vision agent | ||||
| GitHub - roboflow/rf-detr: RF-DETR is a real-time object detection model architecture developed by Roboflow, SOTA on COCO and designed for fine-tuning. | ||||
| 计算机视觉鸟类数量统计 | ||||
| 微信公众平台 | ||||
| 到底是用YOLO还是VLM模型更好? |
Demo

MLOps
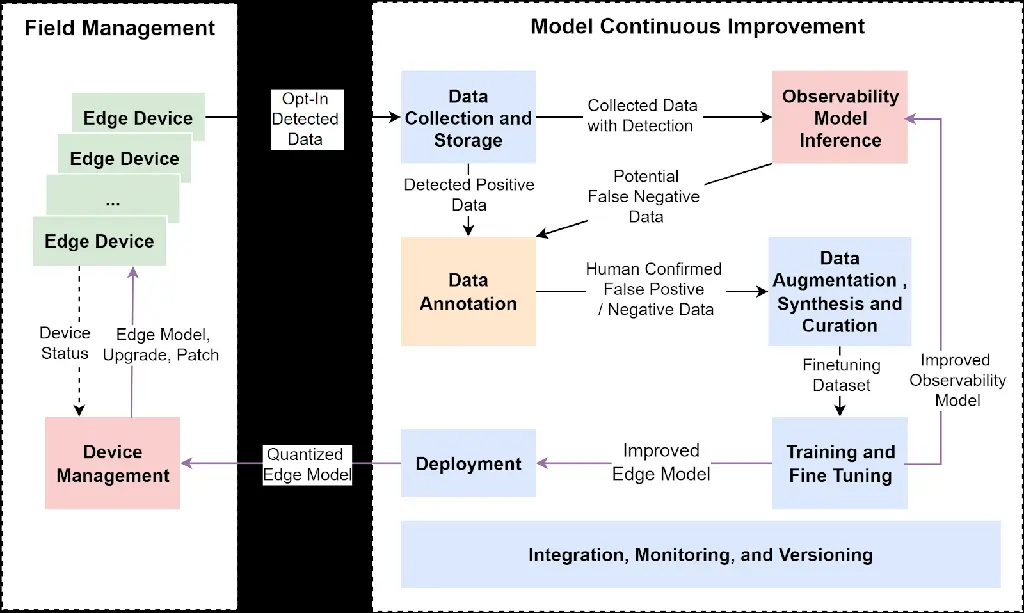
Edge MLOps: Architecture, Challenges, and Platform - SiMa : SiMa
EdgeAI MLOPs
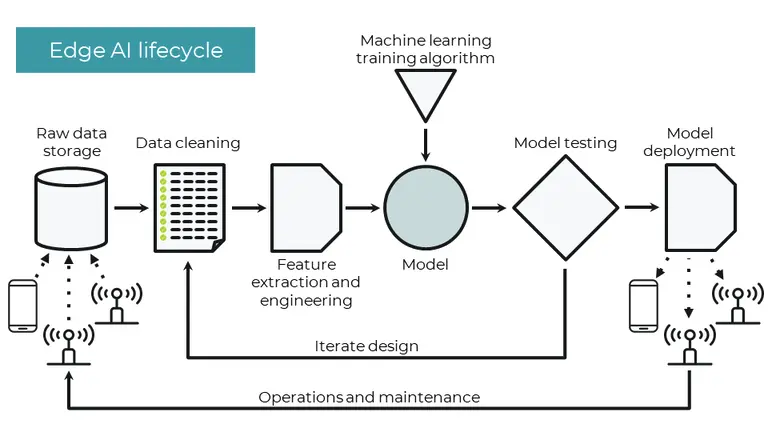
What is edge MLOps? | Edge Impulse Documentation
MLOps and Edge Impulse
Egde Impulse with nVidia Jetson
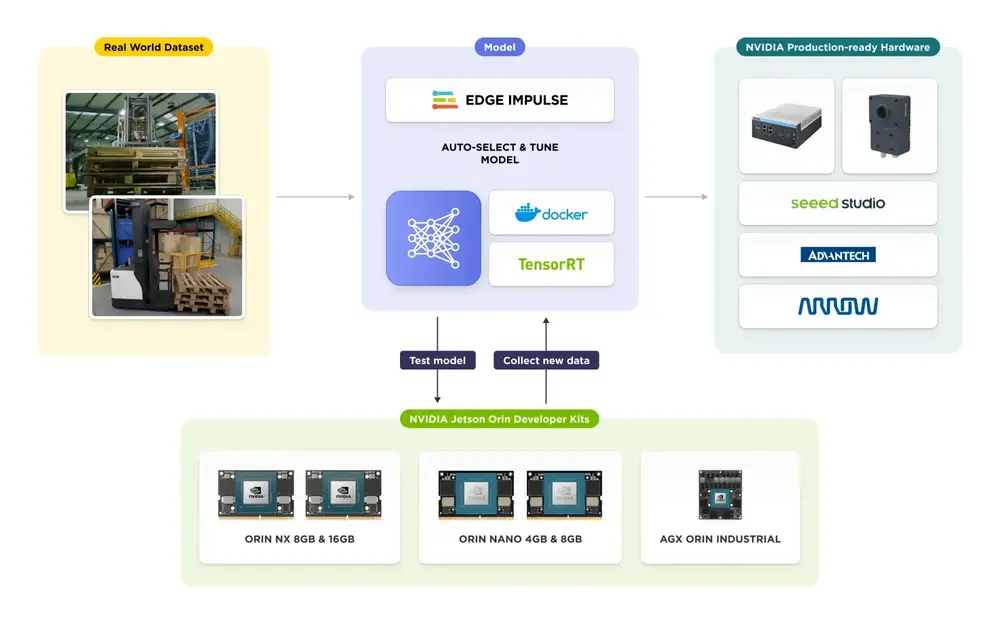
Edge Impulse Optimizes NVIDIA AI for the Edge
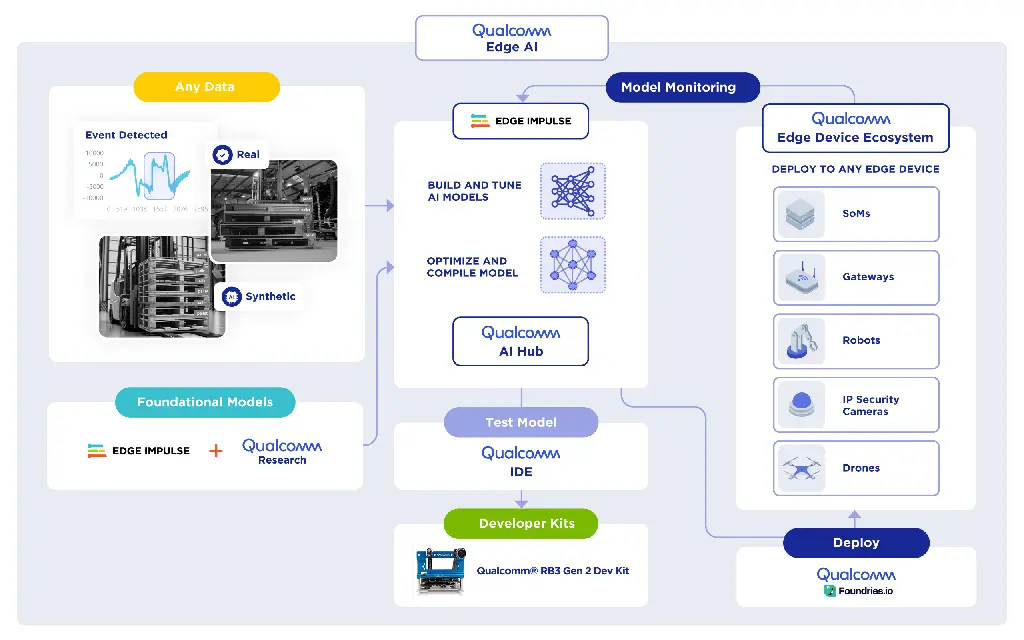
Egde Impulse with Qualcomm
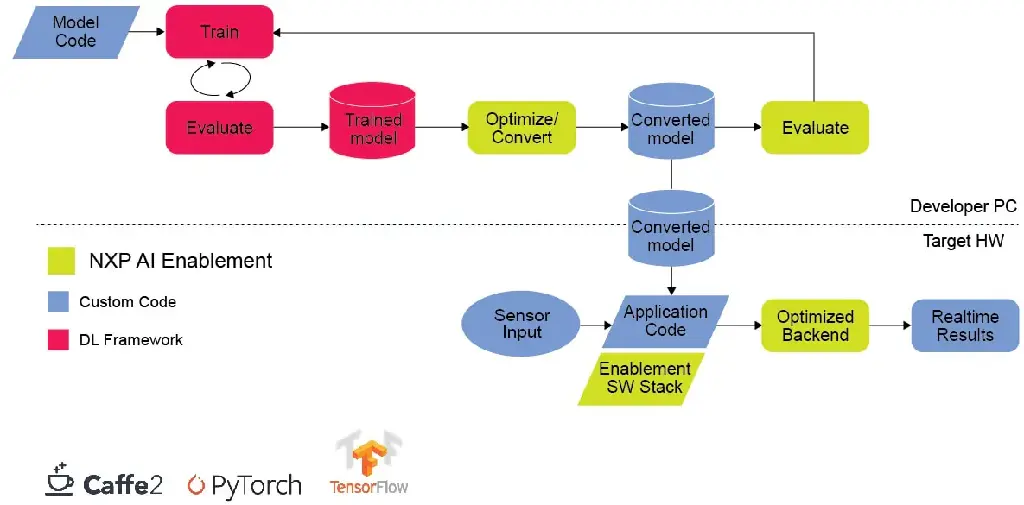
NXP eIQ
Industrial control
Node-RED
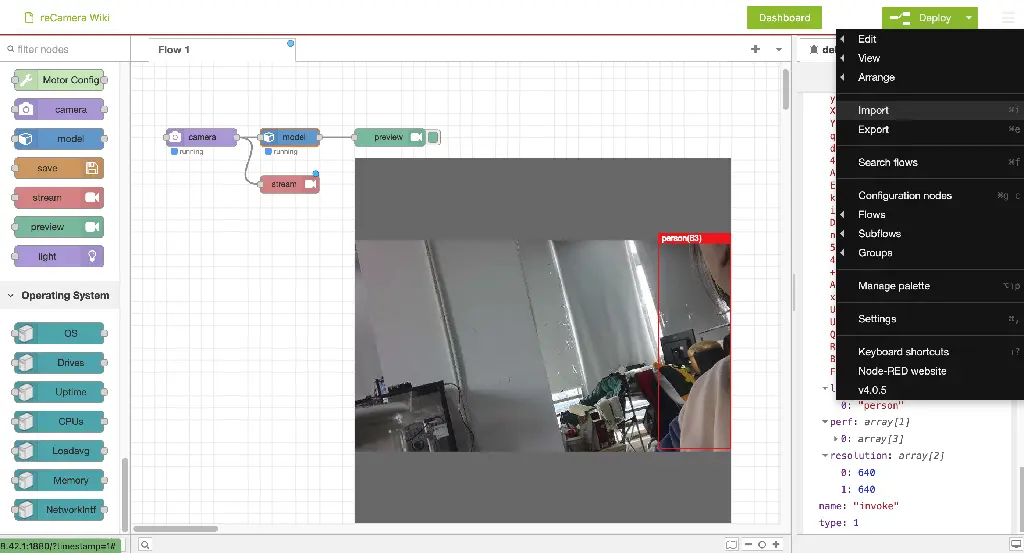
Communicate with PLC
Ethercat
Modbus